Introduction
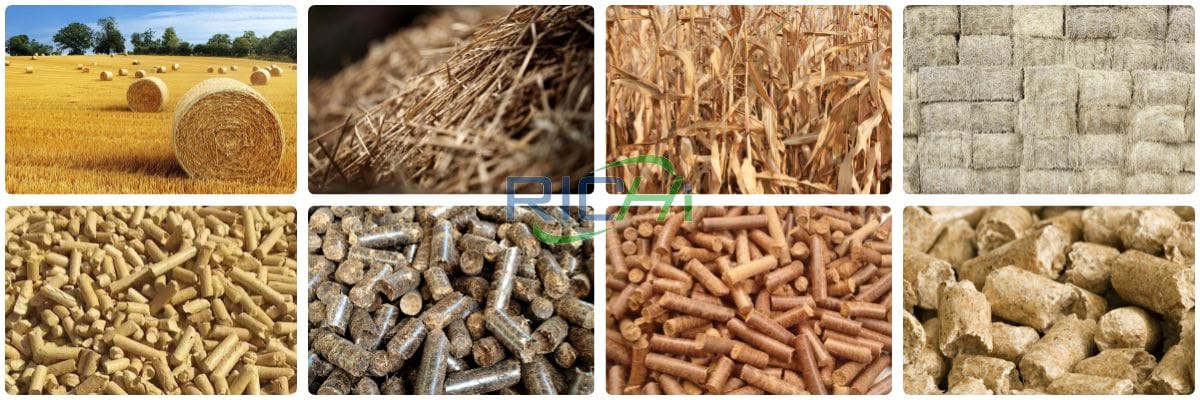
Sawdust is one of the most abundant by-products of the global wood-processing industry. For decades, it was often treated as low-value waste, requiring disposal through landfilling or open burning. With the growing emphasis on renewable energy, waste reduction, and circular resource utilization, sawdust has gained new importance as a valuable biomass material. As a result, interest in the term sawdust pellet mill for sale has increased steadily across industrial, agricultural, and energy-related sectors.
A sawdust pellet machine is not simply a commercial product; it represents a technological solution that converts fine wood residues into dense, standardized pellets suitable for fuel and other applications. This article presents an encyclopedic overview of sawdust pellet machines, covering their historical development, technical principles, structural components, raw material requirements, applications, and role in the global biomass economy.
Historical Development of Sawdust Pellet Machines
The concept of densifying wood residues emerged during the early industrial period, particularly in Europe, where expanding sawmills generated large quantities of sawdust. Early efforts focused on briquetting, producing large blocks that were difficult to transport and use efficiently.
Modern pelletization technology developed in the mid-20th century, supported by advances in mechanical engineering and material science. The transition from briquettes to small cylindrical pellets significantly improved fuel handling, storage, and combustion performance. Over time, the availability of a sawdust pellet machine for sale became closely linked to the expansion of biomass heating systems and renewable energy policies worldwide.
Definition and Function of a Sawdust Pellet Machine
A sawdust pellet machine is an industrial device designed to compress finely processed wood particles into uniform cylindrical pellets under high pressure. These pellets are typically used as biomass fuel, although they may also serve non-energy purposes.
Compared with loose sawdust, pelletized sawdust offers:
Higher energy density
Reduced transportation volume
Consistent size and shape
Improved combustion efficiency
The pellet machine operates as the core unit in a pellet production line, which may include drying, grinding, cooling, and screening systems.
Main Structural Components
Feeding and Material Handling System
Sawdust is lightweight and prone to bridging, requiring specialized feeding systems. Many pellet machines use force-feeding mechanisms to ensure stable and continuous material flow into the pelletizing chamber.
Pelletizing Die Assembly
The die determines pellet size, density, and surface quality. Ring die pellet machines are commonly used in industrial applications due to their high output and durability, while flat die machines are more common in small-scale setups.
Roller Compression System
Rollers rotate against the die surface, applying intense pressure that forces sawdust through the die holes. During this process, natural lignin in the wood softens and acts as a binder.
Power and Transmission System
Electric motors, gearboxes, and drive couplings provide the energy required for pellet formation. Modern designs emphasize torque stability, efficiency, and operational reliability.
Working Principle of Pellet Formation
The pelletizing process relies on mechanical densification rather than chemical bonding. Properly prepared sawdust—typically with a moisture content between 10% and 15%—is fed into the pellet machine. https://richipelletizer.com/sawdust-pellet-mill/
As pressure and friction increase:
Temperature rises inside the die
Lignin becomes plasticized
Wood particles bond together
Pellets are then cut to length and cooled, stabilizing their structure and improving durability.
Raw Material Requirements and Preparation
Sawdust used for pellet production may originate from softwood or hardwood species. However, consistency is critical for efficient pelletizing.
Key preparation factors include:
Uniform particle size
Controlled moisture content
Removal of contaminants such as metal or stones
Pre-processing steps such as drying and fine grinding significantly influence pellet quality and machine performance.
Applications of Sawdust Pellets
Renewable Energy and Heating
Sawdust pellets are widely used in residential pellet stoves, commercial boilers, and district heating systems. Their uniform size enables automated feeding and stable combustion.
Industrial Biomass Power
Large-scale biomass power plants use sawdust pellets as a primary fuel or as a co-firing material with coal to reduce emissions.
Non-Energy Uses
In some regions, sawdust pellets are also used as animal bedding or absorbent materials, benefiting from low dust content and high absorbency.
Global Market and Availability
The global market for pellet machinery has expanded in parallel with renewable energy adoption. Regions with strong forestry industries, such as Europe, North America, and parts of Asia, are major consumers of pellet equipment.
The phrase sawdust pellet machine for sale reflects both local manufacturing and international trade. Equipment suppliers range from small regional workshops to global manufacturers. Companies such as RICHI Pellet Mill have contributed to international biomass projects by supplying pellet machines designed for different production scales.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Pelletizing sawdust reduces waste and supports the use of renewable biomass resources. When sourced from sustainably managed forestry operations or wood-processing residues, sawdust pellets are generally considered low-carbon fuels.
The use of pellet machines also reduces open dumping and burning of sawdust, contributing to improved environmental and workplace conditions.
Maintenance and Operational Longevity
A sawdust pellet machine requires regular maintenance to ensure stable long-term operation. Common maintenance practices include:
Inspection of dies and rollers
Lubrication of bearings and gear systems
Monitoring of temperature and vibration
Replacement of worn components
Manufacturers like RICHI emphasize durable materials and standardized components to enhance equipment lifespan and reduce downtime.
Technological Trends and Future Outlook
Pellet machine technology continues to evolve in response to energy efficiency and automation demands. Emerging trends include:
Intelligent monitoring systems
Energy-saving motors and drives
Wear-resistant alloy dies
Modular production line configurations
As global biomass utilization increases, sawdust pellet machines are expected to remain a key technology in sustainable energy systems. Link
Conclusion
The availability of a sawdust pellet machine for sale reflects the growing importance of biomass pelletizing in modern industry. By transforming sawdust from waste into valuable fuel, pellet machines contribute to renewable energy development and resource efficiency.
Understanding the technical principles, applications, and market context of sawdust pellet machines allows industries and communities to make informed decisions aligned with environmental and economic goals. Sawdust pellet making machine germany