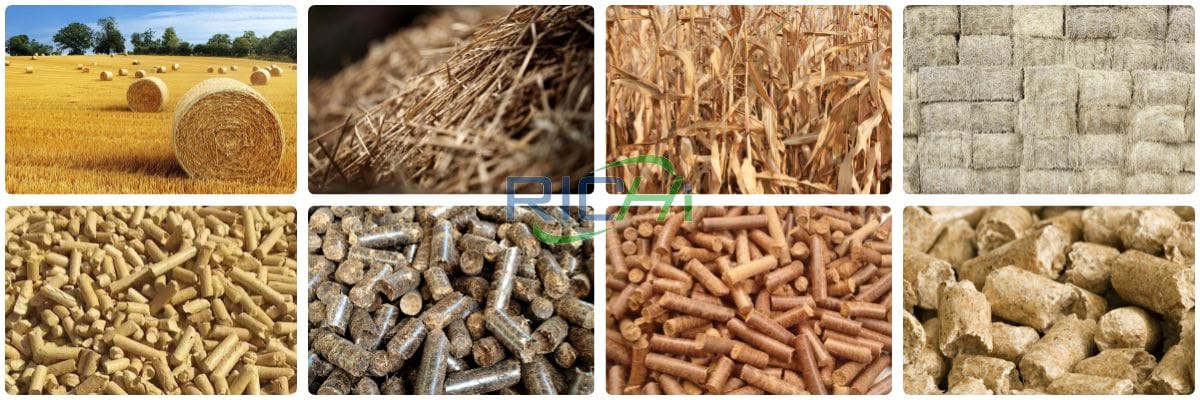
The Straw Pellet Production Line is designed to convert various agricultural and forestry residues into compact, high-density pellets. While primarily intended for straw, this production line can process a variety of biomass materials, making it a valuable asset in the renewable energy and sustainable agriculture sectors. Here’s a look at the different types of pellets that can be produced using a Straw Pellet Production Line and their applications.
Types of Pellets Processed by Straw Pellet Production Line
- Straw Pellets: The primary material processed is straw from crops such as wheat, rice, corn, and barley.
- Hay Pellets: Similar to straw, hay from grasses can be effectively pelletized.
- Corn Stalk Pellets: The stalks left after corn harvesting can be processed into pellets.
- Soybean Stalk Pellets: Like corn stalks, soybean stalks can be pelletized after harvest.
- Cotton Stalk Pellets: Cotton stalks, often considered waste, can be transformed into useful pellets.
- Wood Sawdust Pellets: Many straw pellet production lines can also process wood sawdust into pellets.
- Wood Chip Pellets: Small wood chips, often from forestry residues, can be pelletized using this equipment.
- Bamboo Waste Pellets: Bamboo processing waste can be effectively converted into pellets.
- Peanut Shell Pellets: The shells from peanut processing can be pelletized, turning waste into a valuable resource.
- Sunflower Stalk Pellets: Stalks remaining after sunflower harvest can be processed into pellets.
Related post: straw pellet plant
Uses of Pellets Produced by Straw Pellet Production Line
The pellets produced by a Straw Pellet Production Line have a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Biofuel for Heating:
- Residential Pellet Stoves
- Industrial Boilers
- District Heating Systems
- Power Generation:
- Used in power plants as a co-firing fuel with coal or as the primary fuel in biomass power plants.
- Agricultural Applications:
- Soil Amendment: Improves soil structure and water retention when mixed with soil.
- Mulch: Acts as biodegradable mulch in gardening and agriculture.
- Animal Bedding: Particularly effective for bedding in livestock farming.
- Industrial Processes:
- Used as a renewable fuel source in various manufacturing processes, reducing carbon footprints.
- Cooking Fuel:
- In some regions, these pellets serve as a cleaner alternative to traditional cooking fuels like wood or charcoal.
- Animal Feed:
- Certain types of pellets, especially those made from hay or high-quality straw, can be used in animal feed formulations.
- Absorbents:
- Effective for:
- Oil spill cleanup
- Cat litter
- Industrial spill management
- Effective for:
- Packaging Material:
- Some industries use these pellets as eco-friendly packaging material, replacing plastic-based options.
- Composting:
- Accelerates decomposition and enriches compost with valuable nutrients.
- Erosion Control:
- Used in landscaping and construction for erosion control on slopes and newly seeded areas.
- Bioplastic Production:
- Pellets high in cellulose are explored as raw materials for bioplastics.
- Paper Production:
- Pellets made from wood or bamboo can be used as a fiber source in paper production.
Benefits of Using Straw Pellet Production Line
The versatility of the Straw Pellet Production Line offers several benefits:
- Waste Reduction: Converts agricultural and forestry waste into valuable products.
- Renewable Energy: Produces a sustainable, carbon-neutral fuel source.
- Income Diversification: Provides farmers with an additional income stream from crop residues.
- Reduced Transportation Costs: Increases density for more efficient transportation.
- Storage Efficiency: Requires less storage space compared to loose biomass.
- Consistent Quality: Produces uniform pellets for reliable performance.
Challenges and Considerations
While the Straw Pellet Production Line offers numerous advantages, there are challenges to consider:
- Moisture Content: Different materials may require adjustments in the production process to manage varying moisture levels.
- Pellet Durability: Ensuring consistent pellet quality across different raw materials can be challenging.
- Equipment Wear: Processing abrasive materials may lead to increased wear on machinery components.
- Market Demand: Local market demand for different types of pellets can vary, affecting economic viability.
Conclusion
The Straw Pellet Production Line demonstrates remarkable versatility in processing a wide range of agricultural and forestry residues into valuable pellets. From straw and wood waste to various crop residues, this production line can create pellets suitable for diverse applications, including renewable energy, agriculture, industrial processes, and environmental management.
As the world increasingly focuses on sustainable practices and renewable resources, the importance of such versatile production systems grows. By converting waste into useful products, this technology not only provides economic benefits but also significantly contributes to environmental conservation efforts.
The diverse range of pellets produced and their numerous applications highlight the Straw Pellet Production Line’s role in promoting circular economy principles, reducing waste, lowering carbon emissions, and creating sustainable products for various industries. As research continues and new applications emerge, the potential uses for pellets produced by Straw Pellet Production Lines are likely to expand further, solidifying their place in the sustainable future of industry and agriculture.